News
What Does An Lcd Screen Contain on The Inside?
What Does An Lcd Screen Contain on The Inside?
Content Menu
● Basic Components of an LCD Screen
● Detailed Look at Each Component
>> 1. Backlight
>> 7. Thin Film Transistor (TFT) Matrix
● How LCDs Work: A Step-by-Step Explanation
● Advantages and Disadvantages of LCD
>> 1. What is the purpose of the polarizing filters in an LCD?
>> 2. How do liquid crystals control the brightness of a pixel?
>> 3. What are the different types of backlights used in LCD?
>> 4. What is the function of the color filters in an LCD?
>> 5. What is a TFT matrix, and how does it improve LCD performance?
Introduction
DINGTouch:Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) are ubiquitous in modern technology. From smartphones to televisions, laptops to digital watches, LCD screen are the dominant display technology. Their slim profile, low power consumption (compared to older technologies like CRT), and ability to produce sharp, bright images have made them indispensable. But what exactly is inside an LCD screen? How does it work? This article delves into the internal structure and function of LCD screen, explaining the components and processes that create the images we see.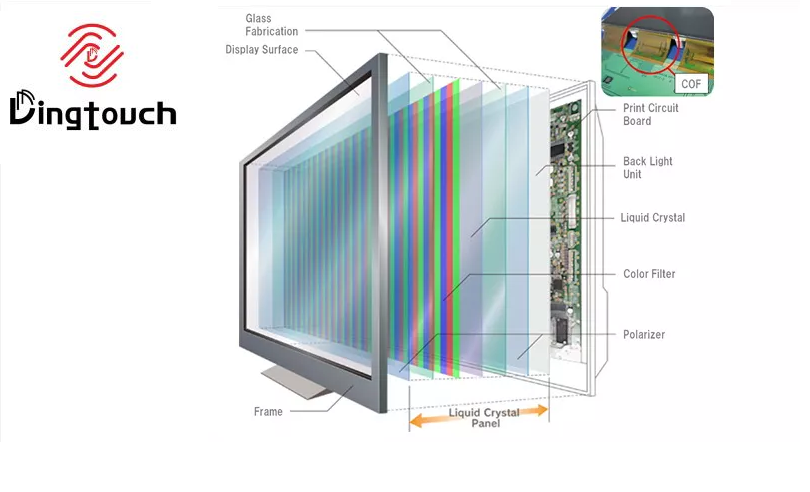
Basic Components of an LCD Screen
An LCD screen is a complex assembly of multiple layers, each with a specific function. The primary components include:
- Backlight: The light source for the display. LCD do not produce their own light; they require an external light source to be visible.
- Polarizing Filters: These filters control the direction of light waves, ensuring that light passes through the liquid crystal layer in a controlled manner.
- Glass Substrates: Transparent glass layers that sandwich the liquid crystal layer and provide a stable structure.
- Electrodes: Conductive layers that apply an electric field to the liquid crystal, controlling the orientation of the liquid crystal molecules.
- Liquid Crystal Layer: The heart of the LCD, this layer contains liquid crystal molecules that change their orientation in response to an electric field, modulating the passage of light.
- Color Filters: These filters add color to the image by selectively transmitting red, green, and blue light.
- Thin Film Transistor (TFT) Matrix (in active matrix LCD): An array of transistors that control the voltage applied to each pixel, enabling precise control over the image.
Detailed Look at Each Component
1. Backlight
The backlight is essential because LCD do not emit light themselves. The backlight shines light through the subsequent layers of the LCD, making the image visible. Common types of backlights include:
- LED (Light Emitting Diode): LED are the most common type of backlight in modern LCD due to their energy efficiency, long lifespan, and compact size.
- CCFL (Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamp): CCFL were used in older LCD but are less common now due to their higher power consumption and shorter lifespan.
2. Polarizing Filters
Polarizing filters are crucial for the operation of LCD. They work by only allowing light waves that are aligned in a specific direction to pass through. An LCD typically has two polarizing filters:
- Vertical Polarizer: This filter only allows vertically aligned light to pass through.
- Horizontal Polarizer: This filter only allows horizontally aligned light to pass through.
The polarizers are oriented at 90 degrees to each other. When light passes through the first polarizer, it becomes polarized in one direction. The liquid crystal layer then twists the light, and the second polarizer either allows or blocks the light based on the twist.
3. Glass Substrates
The glass substrates are transparent layers that provide a stable and flat surface for the other components. These substrates are coated with a thin layer of indium tin oxide (ITO), which acts as an electrode. The ITO layer is patterned to create the individual electrodes that control the voltage applied to the liquid crystal.
4. Electrodes
Electrodes are conductive layers that apply an electric field to the liquid crystal layer. By controlling the voltage applied to the electrodes, the orientation of the liquid crystal molecules can be precisely controlled. The electrodes are typically made of indium tin oxide (ITO), a transparent and conductive material.
5. Liquid Crystal Layer
The liquid crystal layer is the heart of the LCD. Liquid crystals are substances that have properties between those of a conventional liquid and a solid crystal. They can flow like a liquid but have their molecules arranged in an ordered structure like a crystal.
In an LCD, the liquid crystal molecules are typically aligned in a twisted nematic (TN) configuration. When an electric field is applied, the molecules untwist, changing the polarization of light passing through the layer. This change in polarization is what allows the LCD to control the brightness of each pixel[1].
6. Color Filters
Color filters are used to create color images. Each pixel on an LCD screen is divided into three sub-pixels: red, green, and blue (RGB). Each sub-pixel has a color filter that only allows light of that color to pass through. By controlling the brightness of each sub-pixel, the LCD can create a wide range of colors.
7. Thin Film Transistor (TFT) Matrix
In active matrix LCD, a thin film transistor (TFT) is used to control the voltage applied to each pixel. The TFT matrix allows for precise and rapid control of each pixel, resulting in sharper images and faster response times. Active matrix LCDs are also known as TFT-LCD.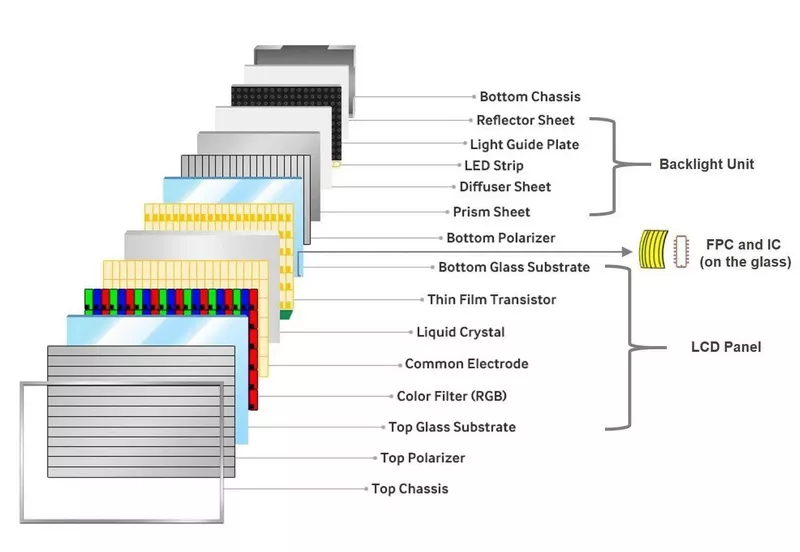
How LCD Work: A Step-by-Step Explanation
1. Backlight Illumination: The backlight emits white light.
2. Polarization: The light passes through the first polarizing filter, becoming polarized in one direction.
3. Liquid Crystal Modulation: The polarized light passes through the liquid crystal layer, where the molecules twist the light based on the applied electric field.
4. Second Polarization: The twisted light passes through the second polarizing filter, which either allows or blocks the light depending on the amount of twist.
5. Color Filtering: The light passes through the color filters, creating red, green, and blue sub-pixels.
6. Image Formation: The combination of the sub-pixels creates the final image.
Types of LCD
There are several types of LCD, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
- TN (Twisted Nematic): TN panels are the oldest and most common type of LCD. They have fast response times but limited viewing angles and color accuracy.
- IPS (In-Plane Switching): IPS panels offer better viewing angles and color accuracy than TN panels but typically have slower response times.
- VA (Vertical Alignment): VA panels offer high contrast ratios and good viewing angles but can suffer from ghosting or blurring in fast-moving scene.
Advantages and Disadvantages of LCD
Advantages:
- Slim Profile: LCD are much thinner and lighter than older display technologies like CRT.
- Low Power Consumption: LCD consume less power than CRT and some other display technologies.
- Sharp Images: LCD can produce sharp and detailed images.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Viewing Angles: Some LCD, particularly TN panels, have limited viewing angles.
- Backlight Requirement: LCD require a backlight, which can add to the cost and complexity of the display.
- Black Levels: LCD can struggle to produce true black colors, as some light always leaks through the liquid crystal layer.
Conclusion
LCD screen are marvels of modern engineering, combining multiple layers of specialized materials to create the images we see every day. From the backlight that illuminates the display to the liquid crystals that modulate the light and the color filters that add vibrancy, each component plays a crucial role. Understanding the internal structure of an LCD screen provides a greater appreciation for the technology that powers our devices.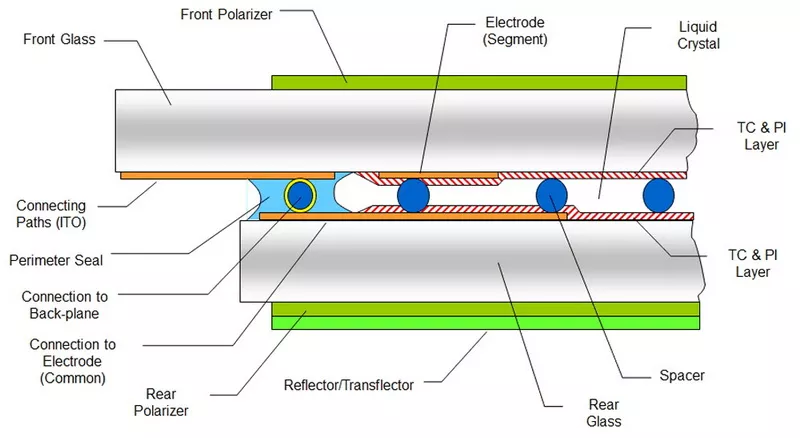
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the purpose of the polarizing filters in an LCD?
The polarizing filters control the direction of light waves, ensuring that light passes through the liquid crystal layer in a controlled manner. They work by only allowing light waves that are aligned in a specific direction to pass through.
2. How do liquid crystals control the brightness of a pixel?
Liquid crystal molecules change their orientation in response to an electric field, modulating the polarization of light passing through the layer. This change in polarization is what allows the LCD to control the brightness of each pixel.
3. What are the different types of backlights used in LCD?
Common types of backlights include LED (Light Emitting Diode) and CCFL (Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamp). LED are the most common type in modern LCD due to their energy efficiency and long lifespan.
4. What is the function of the color filters in an LCD?
Color filters are used to create color images. Each pixel on an LCD screen is divided into three sub-pixels: red, green, and blue (RGB). Each sub-pixel has a color filter that only allows light of that color to pass through.
5. What is a TFT matrix, and how does it improve LCD performance?
In active matrix LCD, a thin film transistor (TFT) is used to control the voltage applied to each pixel. The TFT matrix allows for precise and rapid control of each pixel, resulting in sharper images and faster response times. Active matrix LCD are also known as TFT-LCD.
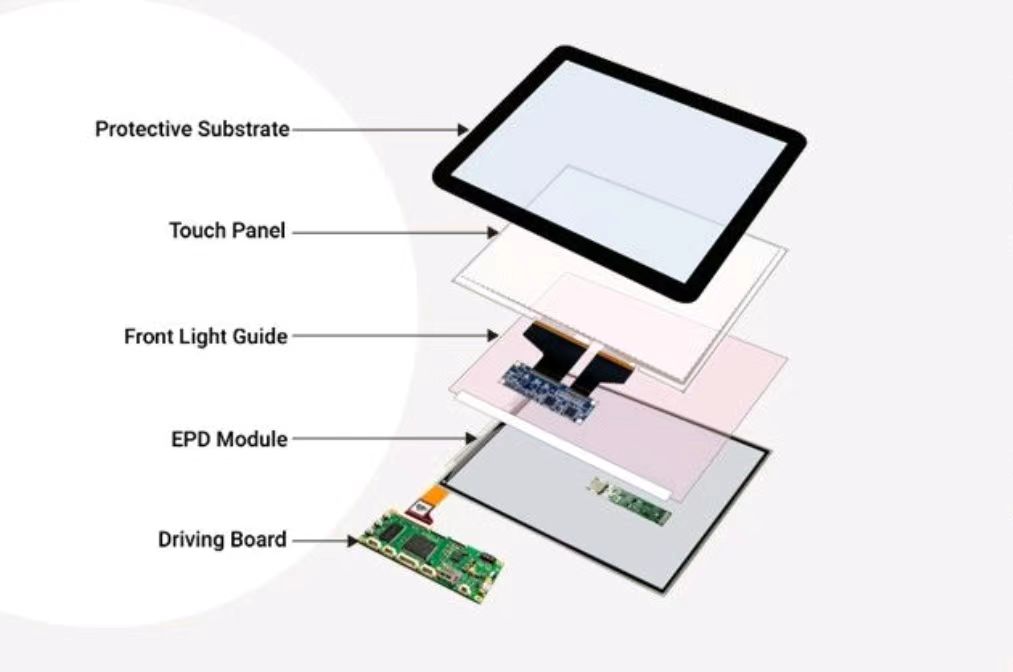
DINGTouch: Committed to continuous innovation and improvement of product quality to meet customers' high requirements and expectations.
DINGTouch is a manufacturer that provides high quality touch screen panels. Focus on the design, manufacturing and sales of touch screen panels, and are committed to providing customized solutions that satisfy customers.
DINGTouch: In the process of customizing touch screen panels, we focus on close cooperation and communication with customers. Understanding customers' needs and providing customized solutions will meet customers' individual needs. The company's products are favored by customers for their high quality and reliability, and provide them with the best touchscreen panel solutions.
At DINGTOUCH, we are the world's leading touchscreen manufacturer, helping businesses around the world take advantage of this exciting technology. For more information, please visit the home page now.
Find the DINGTouch technical team to achieve the success of your company's new project.
How to choose touch screen customization?
DINGTouch is a company specializing in the R&D and production of touch screen technology, headquartered in Shenzhen, China. As a professional touch screen supplier, DINGTouch is committed to providing high-quality, stable and reliable touch screen products to meet the diverse needs of customers. We continue to carry out technological innovation and product optimization to ensure that its touch screen products have good sensitivity, accuracy and durability.
In addition to the products themselves, we also focus on cooperation and communication with customers, and are committed to providing customized solutions and excellent after-sales services. Through continuous efforts to improve product quality and customer satisfaction, we have established a good reputation in the touchscreen industry and won widespread market recognition.
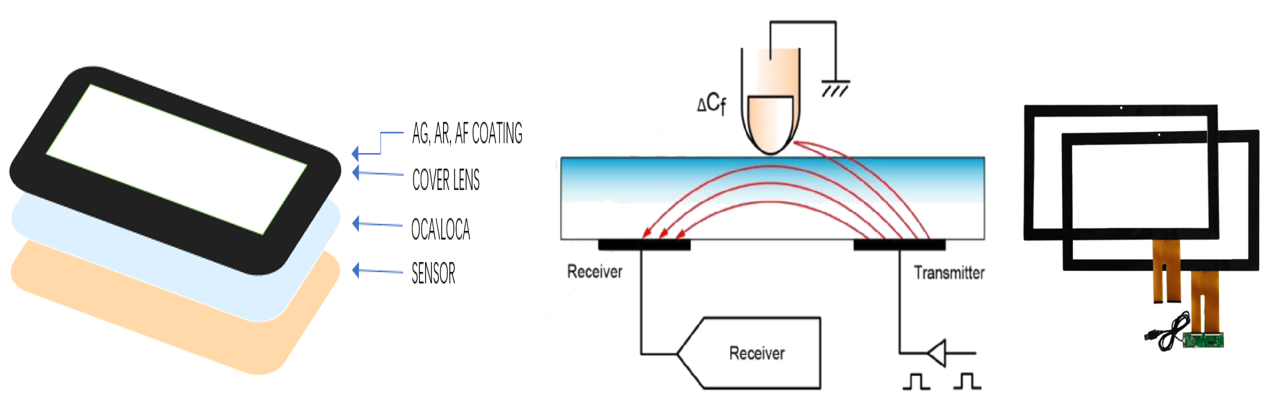
What DINGTOUCH can do:
• PCAP maximum size 65”
• Multi-touch (Touch screen can be customized to your needs.)
• Optical bonding service/air bonding
• LCD interface: HDMI/RGB/MIPI/LVDS/EDP, etc.
• PCAP interface: IIC/USB interface
• CTP can customize the cover glass surface treatment process AG (anti-glare), AR (anti-reflection), AF (anti-fingerprint), waterproof, and glove touch
• Supports 0.55 mm-12 mm coverslip touch.
• Support operating temperature: -40℃-90℃.
Dingtouch Industrial Capacitive Touch Screen Manufacturer
In conclusion, Dingtouch as a professional touch screen manufacturer with more than 10 years touch screen experience.We have many capacitive touch screen. Such as5 inch touch screen,7 inch touch screen,10.1inch touch screen,15 inch touch screen,15.6 inch touch screen,17 inch touch screen,18.5 inch touch screen,19 inch touch screen,21.5 inch touch screen,32 inch touch screen, However, we also welcome to customize your own touch screen . Contact our team today to learn what capacitive touch screen are best for our retail business needs.
Contact us NOW! sales@szdingtouch.com
DINGTouch: Committed to continuous innovation and improvement of product quality to meet customers' high requirements and expectations.
DINGTouch is a manufacturer that provides high quality touch screen panels. Focus on the design, manufacturing and sales of touch screen panels, and are committed to providing customized solutions that satisfy customers.
DINGTouch: In the process of customizing touch screen panels, we focus on close cooperation and communication with customers. Understanding customers' needs and providing customized solutions will meet customers' individual needs. The company's products are favored by customers for their high quality and reliability, and provide them with the best touchscreen panel solutions.
At DINGTOUCH, we are the world's leading touchscreen manufacturer, helping businesses around the world take advantage of this exciting technology. For more information, please visit the home page now.
Find the DINGTouch technical team to achieve the success of your company's new project.
How to choose touch screen customization?
DINGTouch is a company specializing in the R&D and production of touch screen technology, headquartered in Shenzhen, China. As a professional touch screen supplier, DINGTouch is committed to providing high-quality, stable and reliable touch screen products to meet the diverse needs of customers. We continue to carry out technological innovation and product optimization to ensure that its touch screen products have good sensitivity, accuracy and durability.
In addition to the products themselves, we also focus on cooperation and communication with customers, and are committed to providing customized solutions and excellent after-sales services. Through continuous efforts to improve product quality and customer satisfaction, we have established a good reputation in the touchscreen industry and won widespread market recognition.
What DINGTOUCH can do:
• PCAP maximum size 65”
• Multi-touch (Touch screen can be customized to your needs.)
• Optical bonding service/air bonding
• LCD interface: HDMI/RGB/MIPI/LVDS/EDP, etc.
• PCAP interface: IIC/USB interface
• CTP can customize the cover glass surface treatment process AG (anti-glare), AR (anti-reflection), AF (anti-fingerprint), waterproof, and glove touch
• Supports 0.55 mm-12 mm coverslip touch.
• Support operating temperature: -40℃-90℃.
Dingtouch Industrial Capacitive Touch Screen Manufacturer
In conclusion, Dingtouch as a professional touch screen manufacturer with more than 10 years touch screen experience.We have many capacitive touch screen. Such as5 inch touch screen,7 inch touch screen,10.1inch touch screen,15 inch touch screen,15.6 inch touch screen,17 inch touch screen,18.5 inch touch screen,19 inch touch screen,21.5 inch touch screen,32 inch touch screen, However, we also welcome to customize your own touch screen . Contact our team today to learn what capacitive touch screen are best for our retail business needs.
Contact us NOW! sales@szdingtouch.com
CATEGORIES
CONTACT US
Contact: Dingtouch
Phone: +8615815536116
Tel: +8615815536116
Email: sales@szdingtouch.com
Add: Building A, Bailu Plaza, No. 48, Gonghe Industrial Road, Gongle Community, Xixiang Street, Baoan District, Shenzhen,China. 518126



 Dingtouch
Dingtouch